Learn more about how degenerative disc disease develops.
Degenerative disc disease occurs when discs in the spine begin to break down or move out of place. Inter-vertebral discs are found between individual vertebrae and act as shock absorbers.
- When the discs start degenerating, they stiffen and cause pain
- Stiff and painful discs restrict back movement
Causes
Degenerative disc disease does not have one specific cause. It may be caused by normal physical back strains or trauma. Everybody is susceptible to getting degenerative spine diseases, but some people develop the condition earlier than others do. Although anyone can get degenerative disc disease, this condition is usually common with older patients. The most common symptom for the disease is pain in the lower back, neck, arms, or legs. It is important to know that the symptoms often vary in nature and severity. In addition, degenerative disc diseases have different treatments. Some treatments may involve physical therapy and rest, while others are invasive and may involve administering spinal injections and surgery.
Symptoms
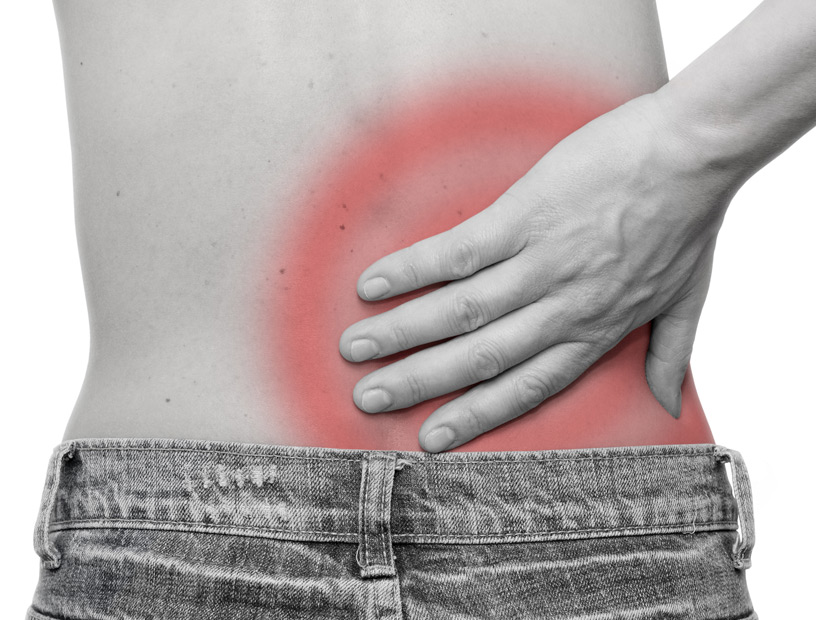
Back pain is the key symptom of degenerative spinal disease. This pain originates from the middle of the back, where it is usually the strongest. As the discs begin slipping out of place, they add pressure on the nerves resulting in “referred pain.” Referred pain originates from a particular spot but felt in another part of the body. Sciatica is an example of referred pain caused by degenerative disc disease. The largest nerve found in the human body is the sciatic nerve. It begins at the back and branches downwards towards the legs. When pressure is added on the sciatic nerve, pain is not experienced on the back, but on the legs or buttocks.
Prevention
It is important to implement early lifestyle changes to prevent degenerative disc disease. These will go a long way in preventing toxic or harmful substances from causing weaknesses on the spine. Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol because it diminishes bone health and accelerates bone destruction respectively. In addition, exercise regularly to reduce weight and avoid straining the back.
Eat healthy foods that help to regenerate the bones. A diet consisting of fruits, grains, and vegetables is often recommended. Some of the foods that can help prevent degenerative spine diseases include fish, poultry, lentil, beans, and tofu. Avoid eating excessive amounts of meat and drinking artificially sweetened soft drinks.
Maintain a good posture at all times to prevent premature development of degenerative spinal diseases. Good posture helps to ensure that you do not strain the vertebral bones. Bend your knees when lifting a heavy object and carry the object as close to your body as possible. Sitting and standing for long periods also puts a strain on your back. Finally, be sure to use a high-density mattress for sleeping.
Treatments
Degenerative disc disease is often treated with non-invasive treatment options including anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy. However, other treatment options, including surgery, may be required to treat multi-level degenerative disc diseases. In 2008, The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of artificial discs in the treatment of degenerative disc disease.

on caring for specific orthopedic needs.